Niacin, an essential nutrient belonging to the B-vitamin family, is pivotal in supporting various bodily functions. A deficiency in this vital nutrient can lead to multiple symptoms that affect the skin, digestive system, and nervous system.
Dermatological Symptoms
The skin often bears the initial signs of niacin deficiency. Dermatitis, a condition marked by redness, inflammation, and heightened sensitivity to sunlight, is a common early symptom. The skin may become rough and scaly and develop a darkened rash, especially in sun-exposed areas. These manifestations often resemble a sunburn and may progress if the deficiency persists.
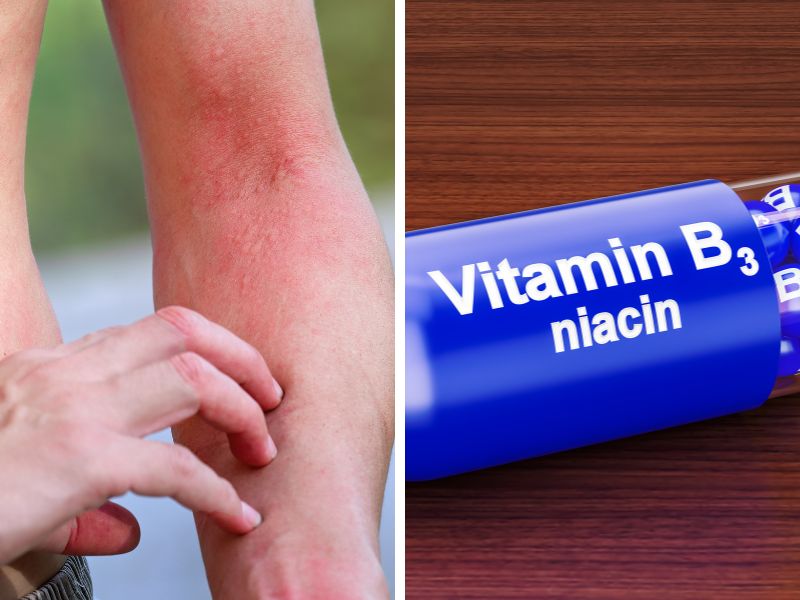
Image Credit: Canva. com
Gastrointestinal Distress
Niacin deficiency also impacts the digestive system, resulting in gastrointestinal symptoms. Individuals may experience diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. These symptoms contribute to nutrient malabsorption, exacerbating the deficiency and potentially leading to further complications.
Neurological Manifestations
As the deficiency progresses, neurological symptoms emerge. Confusion, memory impairment, and depression are frequently observed. In severe cases, individuals might experience hallucinations and psychosis. Peripheral neuropathy, characterized by tingling sensations or numbness in the extremities, can also occur, significantly affecting mobility and sensation.
Causes And Risk Factors
Niacin deficiency primarily arises from inadequate dietary intake, especially in populations reliant on diets lacking in niacin-rich foods like meats, fish, nuts, and whole grains. Conditions affecting nutrient absorption, such as Crohn’s disease or alcoholism, can elevate the risk of deficiency. Additionally, certain medications might interfere with niacin absorption or utilization in the body.
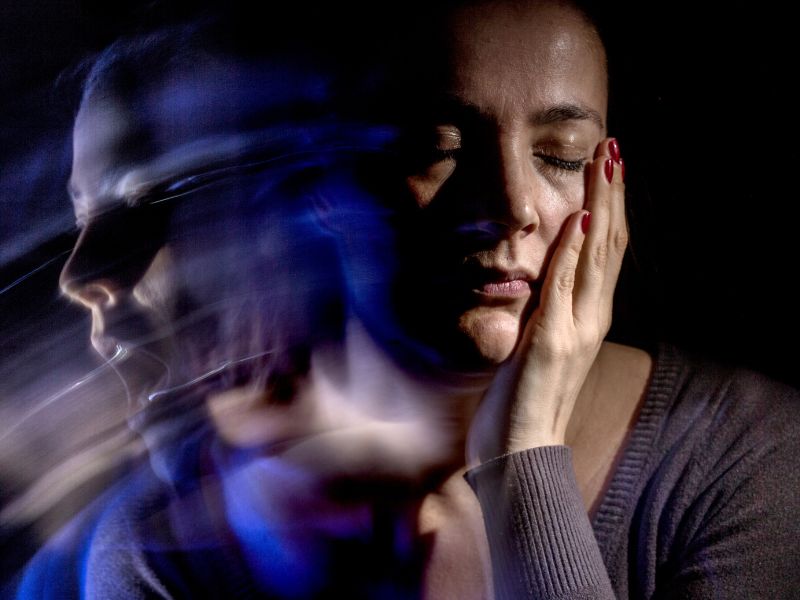

Image Credit: Canva. com
Diagnosis And Treatment
Diagnosing niacin deficiency involves a thorough assessment by healthcare professionals, including physical examinations and possibly blood tests to measure niacin levels. Treatment focuses on dietary adjustments, incorporating niacin-rich foods or supplements as necessary. Severe cases may require prescription-strength supplements.
Prevention
Preventing niacin deficiency involves maintaining a balanced diet rich in niacin sources. Regular health check-ups and awareness of personal health conditions that might impact nutrient absorption are vital preventive measures.
